Table of Contents
- 1. Introduction
- 2. Design Requirements and Philosophy
- 3. Implementation
- 3.1. Proxy Obedience
- 3.2. State Separation
- 3.3. Disk Avoidance
- 3.4. Application Data Isolation
- 3.5. Cross-Origin Identifier Unlinkability
- 3.6. Cross-Origin Fingerprinting Unlinkability
- 3.7. Long-Term Unlinkability via "New Identity" button
- 3.8. Click-to-play for plugins and invasive content
- 3.9. Description of Firefox Patches
- 4. Packaging
- 5. Testing
This document describes the adversary model, design requirements, implementation, packaging and testing procedures of the Tor Browser. It is current as of Tor Browser 2.2.35-1 and Torbutton 1.4.5.
This document is also meant to serve as a set of design requirements and to describe a reference implementation of a Private Browsing Mode that defends against active network adversaries, in addition to the passive forensic local adversary currently addressed by the major browsers.
A Tor web browser adversary has a number of goals, capabilities, and attack types that can be used to guide us towards a set of requirements for the Tor Browser. Let's start with the goals.
- Bypassing proxy settings
The adversary's primary goal is direct compromise and bypass of Tor, causing the user to directly connect to an IP of the adversary's choosing.
- Correlation of Tor vs Non-Tor Activity
If direct proxy bypass is not possible, the adversary will likely happily settle for the ability to correlate something a user did via Tor with their non-Tor activity. This can be done with cookies, cache identifiers, javascript events, and even CSS. Sometimes the fact that a user uses Tor may be enough for some authorities.
- History disclosure
The adversary may also be interested in history disclosure: the ability to query a user's history to see if they have issued certain censored search queries, or visited censored sites.
- Location information
Location information such as timezone and locality can be useful for the adversary to determine if a user is in fact originating from one of the regions they are attempting to control, or to zero-in on the geographical location of a particular dissident or whistleblower.
- Miscellaneous anonymity set reduction
Anonymity set reduction is also useful in attempting to zero in on a particular individual. If the dissident or whistleblower is using a rare build of Firefox for an obscure operating system, this can be very useful information for tracking them down, or at least tracking their activities.
- History records and other on-disk
information
In some cases, the adversary may opt for a heavy-handed approach, such as seizing the computers of all Tor users in an area (especially after narrowing the field by the above two pieces of information). History records and cache data are the primary goals here.
The adversary can position themselves at a number of different locations in order to execute their attacks.
- Exit Node or Upstream Router
The adversary can run exit nodes, or alternatively, they may control routers upstream of exit nodes. Both of these scenarios have been observed in the wild.
- Ad servers and/or Malicious Websites
The adversary can also run websites, or more likely, they can contract out ad space from a number of different ad servers and inject content that way. For some users, the adversary may be the ad servers themselves. It is not inconceivable that ad servers may try to subvert or reduce a user's anonymity through Tor for marketing purposes.
- Local Network/ISP/Upstream Router
The adversary can also inject malicious content at the user's upstream router when they have Tor disabled, in an attempt to correlate their Tor and Non-Tor activity.
- Physical Access
Some users face adversaries with intermittent or constant physical access. Users in Internet cafes, for example, face such a threat. In addition, in countries where simply using tools like Tor is illegal, users may face confiscation of their computer equipment for excessive Tor usage or just general suspicion.
The adversary can perform the following attacks from a number of different positions to accomplish various aspects of their goals. It should be noted that many of these attacks (especially those involving IP address leakage) are often performed by accident by websites that simply have Javascript, dynamic CSS elements, and plugins. Others are performed by ad servers seeking to correlate users' activity across different IP addresses, and still others are performed by malicious agents on the Tor network and at national firewalls.
- Read and insert identifiers
The browser contains multiple facilities for storing identifiers that the adversary creates for the purposes of tracking users. These identifiers are most obviously cookies, but also include HTTP auth, DOM storage, cached scripts and other elements with embedded identifiers, client certificates, and even TLS Session IDs.
An adversary in a position to perform MITM content alteration can inject document content elements to both read and inject cookies for arbitrary domains. In fact, even many "SSL secured" websites are vulnerable to this sort of active sidejacking. In addition, the ad networks of course perform tracking with cookies as well.
- Fingerprint users based on browser
attributes
There is an absurd amount of information available to websites via attributes of the browser. This information can be used to reduce anonymity set, or even uniquely fingerprint individual users. Fingerprinting is an intimidating problem to attempt to tackle, especially without a metric to determine or at least intuitively understand and estimate which features will most contribute to linkability between visits.
The Panopticlick study done by the EFF uses the actual entropy - the number of identifying bits of information encoded in browser properties - as this metric. Their result data is definitely useful, and the metric is probably the appropriate one for determining how identifying a particular browser property is. However, some quirks of their study means that they do not extract as much information as they could from display information: they only use desktop resolution and do not attempt to infer the size of toolbars. In the other direction, they may be over-counting in some areas, as they did not compute joint entropy over multiple attributes that may exhibit a high degree of correlation. Also, new browser features are added regularly, so the data should not be taken as final.
Despite the uncertainty, all fingerprinting attacks leverage the following attack vectors:
- Observing Request Behavior
Properties of the user's request behavior comprise the bulk of low-hanging fingerprinting targets. These include: User agent, Accept-* headers, pipeline usage, and request ordering. Additionally, the use of custom filters such as AdBlock and other privacy filters can be used to fingerprint request patterns (as an extreme example).
- Inserting Javascript
Javascript can reveal a lot of fingerprinting information. It provides DOM objects such as window.screen and window.navigator to extract information about the useragent. Also, Javascript can be used to query the user's timezone via the
Date()object, WebGL can reveal information about the video card in use, and high precision timing information can be used to fingerprint the CPU and interpreter speed. In the future, new JavaScript features such as Resource Timing may leak an unknown amount of network timing related information. - Inserting Plugins
The Panopticlick project found that the mere list of installed plugins (in navigator.plugins) was sufficient to provide a large degree of fingerprintability. Additionally, plugins are capable of extracting font lists, interface addresses, and other machine information that is beyond what the browser would normally provide to content. In addition, plugins can be used to store unique identifiers that are more difficult to clear than standard cookies. Flash-based cookies fall into this category, but there are likely numerous other examples. Beyond fingerprinting, plugins are also abysmal at obeying the proxy settings of the browser.
- Inserting CSS
CSS media queries can be inserted to gather information about the desktop size, widget size, display type, DPI, user agent type, and other information that was formerly available only to Javascript.
- Observing Request Behavior
- Remotely or locally exploit browser and/or
OS
Last, but definitely not least, the adversary can exploit either general browser vulnerabilities, plugin vulnerabilities, or OS vulnerabilities to install malware and surveillance software. An adversary with physical access can perform similar actions. Regrettably, this last attack capability is outside of our ability to defend against, but it is worth mentioning for completeness. The Tails system however can provide some limited defenses against this adversary.
The Tor Browser Design Requirements are meant to describe the properties of a Private Browsing Mode that defends against both network and local forensic adversaries.
There are two main categories of requirements: Security Requirements, and Privacy Requirements. Security Requirements are the minimum properties in order for a browser to be able to support Tor and similar privacy proxies safely. Privacy requirements are the set of properties that cause us to prefer one browser over another.
While we will endorse the use of browsers that meet the security requirements, it is primarily the privacy requirements that cause us to maintain our own browser distribution.
The key words "MUST", "MUST NOT", "REQUIRED", "SHALL", "SHALL NOT", "SHOULD", "SHOULD NOT", "RECOMMENDED", "MAY", and "OPTIONAL" in this document are to be interpreted as described in RFC 2119.
The security requirements are primarily concerned with ensuring the safe use of Tor. Violations in these properties typically result in serious risk for the user in terms of immediate deanonymization and/or observability. With respect to browser support, security requirements are the minimum properties in order for Tor to support the use of a particular browser.
- Proxy
Obedience
The browser MUST NOT bypass Tor proxy settings for any content.
- State
Separation
The browser MUST NOT provide any stored state to the content window from other browsers or other browsing modes, including shared state from plugins, machine identifiers, and TLS session state.
- Disk
Avoidance
The browser MUST NOT write any information that is derived from or that reveals browsing activity to the disk, or store it in memory beyond the duration of one browsing session, unless the user has explicitly opted to store their browsing history information to disk.
- Application Data
Isolation
The components involved in providing private browsing MUST be self-contained, or MUST provide a mechanism for rapid, complete removal of all evidence of the use of the mode. In other words, the browser MUST NOT write or cause the operating system to write any information about the use of private browsing to disk outside of the application's control. The user must be able to ensure that secure deletion of the software is sufficient to remove evidence of the use of the software. All exceptions and shortcomings due to operating system behavior MUST be wiped by an uninstaller. However, due to permissions issues with access to swap, implementations MAY choose to leave it out of scope, and/or leave it to the Operating System/platform to implement ephemeral-keyed encrypted swap.
The privacy requirements are primarily concerned with reducing linkability: the ability for a user's activity on one site to be linked with their activity on another site without their knowledge or explicit consent. With respect to browser support, privacy requirements are the set of properties that cause us to prefer one browser over another.
For the purposes of the unlinkability requirements of this section as well as the descriptions in the implementation section, a url bar origin means at least the second-level DNS name. For example, for mail.google.com, the origin would be google.com. Implementations MAY, at their option, restrict the url bar origin to be the entire fully qualified domain name.
- Cross-Origin
Identifier Unlinkability
User activity on one url bar origin MUST NOT be linkable to their activity in any other url bar origin by any third party automatically or without user interaction or approval. This requirement specifically applies to linkability from stored browser identifiers, authentication tokens, and shared state. The requirement does not apply to linkable information the user manually submits to sites, or due to information submitted during manual link traversal. This functionality SHOULD NOT interfere with federated login in a substantial way.
- Cross-Origin
Fingerprinting Unlinkability
User activity on one url bar origin MUST NOT be linkable to their activity in any other url bar origin by any third party. This property specifically applies to linkability from fingerprinting browser behavior.
- Long-Term
Unlinkability
The browser SHOULD provide an obvious, easy way to remove all of its authentication tokens and browser state and obtain a fresh identity. Additionally, the browser SHOULD clear linkable state by default automatically upon browser restart, except at user option.
In addition to the above design requirements, the technology decisions about Tor Browser are also guided by some philosophical positions about technology.
- Preserve existing user model
The existing way that the user expects to use a browser must be preserved. If the user has to maintain a different mental model of how the sites they are using behave depending on tab, browser state, or anything else that would not normally be what they experience in their default browser, the user will inevitably be confused. They will make mistakes and reduce their privacy as a result. Worse, they may just stop using the browser, assuming it is broken.
User model breakage was one of the failures of Torbutton: Even if users managed to install everything properly, the toggle model was too hard for the average user to understand, especially in the face of accumulating tabs from multiple states crossed with the current tor-state of the browser.
- Favor the implementation mechanism least likely to
break sites
In general, we try to find solutions to privacy issues that will not induce site breakage, though this is not always possible.
- Plugins must be restricted
Even if plugins always properly used the browser proxy settings (which none of them do) and could not be induced to bypass them (which all of them can), the activities of closed-source plugins are very difficult to audit and control. They can obtain and transmit all manner of system information to websites, often have their own identifier storage for tracking users, and also contribute to fingerprinting.
Therefore, if plugins are to be enabled in private browsing modes, they must be restricted from running automatically on every page (via click-to-play placeholders), and/or be sandboxed to restrict the types of system calls they can execute. If the user decides to craft an exemption to allow a plugin to be used, it MUST only apply to the top level url bar domain, and not to all sites, to reduce linkability.
- Minimize Global Privacy Options
Another failure of Torbutton was (and still is) the options panel. Each option that detectably alters browser behavior can be used as a fingerprinting tool. Similarly, all extensions SHOULD be disabled in the mode except as an opt-in basis. We SHOULD NOT load system-wide addons or plugins.
Instead of global browser privacy options, privacy decisions SHOULD be made per url bar origin to eliminate the possibility of linkability between domains. For example, when a plugin object (or a Javascript access of window.plugins) is present in a page, the user should be given the choice of allowing that plugin object for that url bar origin only. The same goes for exemptions to third party cookie policy, geo-location, and any other privacy permissions.
If the user has indicated they do not care about local history storage, these permissions can be written to disk. Otherwise, they should remain memory-only.
- No filters
Filter-based addons such as AdBlock Plus, Request Policy, Ghostery, Priv3, and Sharemenot are to be avoided. We believe that these addons do not add any real privacy to a proper implementation of the above privacy requirements, as all third parties are prevented from tracking users between sites by the implementation. Filter-based addons can also introduce strange breakage and cause usability nightmares, and will also fail to do their job if an adversary simply registers a new domain or creates a new url path. Worse still, the unique filter sets that each user creates or installs will provide a wealth of fingerprinting targets.
As a general matter, we are also generally opposed to shipping an always-on Ad blocker with Tor Browser. We feel that this would damage our credibility in terms of demonstrating that we are providing privacy through a sound design alone, as well as damage the acceptance of Tor users by sites who support themselves through advertising revenue.
Users are free to install these addons if they wish, but doing so is not recommended, as it will alter the browser request fingerprint.
- Stay Current
We believe that if we do not stay current with the support of new web technologies, we cannot hope to substantially influence or be involved in their proper deployment or privacy realization. However, we will likely disable high-risk features pending analysis, audit, and mitigation.
The Implementation section is divided into subsections, each of which corresponds to a Design Requirement. Each subsection is divided into specific web technologies or properties. The implementation is then described for that property.
In some cases, the implementation meets the design requirements in a non-ideal way (for example, by disabling features). In rare cases, there may be no implementation at all. Both of these cases are denoted by differentiating between the Design Goal and the Implementation Status for each property. Corresponding bugs in the Tor bug tracker are typically linked for these cases.
Proxy obedience is assured through the following:
- Firefox Proxy settings
The Torbutton xpi sets the Firefox proxy settings to use Tor directly as a SOCKS proxy. It sets network.proxy.socks_remote_dns, network.proxy.socks_version, and network.proxy.socks_port.
We have verified that these settings properly proxy HTTPS, OCSP, HTTP, FTP, gopher (now defunct), DNS, SafeBrowsing Queries, all javascript activity, including HTML5 audio and video objects, addon updates, wifi geolocation queries, searchbox queries, XPCOM addon HTTPS/HTTP activity, and live bookmark updates. We have also verified that IPv6 connections are not attempted, through the proxy or otherwise (Tor does not yet support IPv6). We have also verified that external protocol helpers, such as smb urls and other custom protocol handers are all blocked.
Numerous other third parties have also reviewed and tested the proxy settings and have provided test cases based on their work. See in particular decloak.net.
- Disabling plugins
Plugins have the ability to make arbitrary OS system calls and bypass proxy settings. This includes the ability to make UDP sockets and send arbitrary data independent of the browser proxy settings.
Torbutton disables plugins by using the @mozilla.org/plugin/host;1 service to mark the plugin tags as disabled. Additionally, we set plugin.disable_full_page_plugin_for_types to the list of supported mime types for all currently installed plugins.
In addition, to prevent any unproxied activity by plugins at load time, we also patch the Firefox source code to prevent the load of any plugins except for Flash and Gnash.
Finally, even if the user alters their browser settings to re-enable the Flash plugin, we have configured NoScript to provide click-to-play placeholders, so that only desired objects will be loaded, and only after user confirmation.
- External App Blocking
External apps, if launched automatically, can be induced to load files that perform network activity. In order to prevent this, Torbutton installs a component to provide the user with a popup whenever the browser attempts to launch a helper app. Additionally, due primarily to an issue with Ubuntu Unity, url-based drag and drop is filtered by this component. Unity was pre-fetching URLs without using the browser's proxy settings during a drag action, even if the drop was ultimately canceled by the user.
Tor Browser State is separated from existing browser state through use of a custom Firefox profile. Furthermore, plugins are disabled, which prevents Flash cookies from leaking from a pre-existing Flash directory.
Tor Browser MUST (at user option) prevent all disk records of browser activity. The user should be able to optionally enable URL history and other history features if they so desire. Once we simplify the preferences interface, we will likely just enable Private Browsing mode by default to handle this goal.
For now, Tor Browser blocks write access to the disk through Torbutton using several Firefox preferences. The set of prefs is: dom.storage.enabled, browser.cache.memory.enable, network.http.use-cache, browser.cache.disk.enable, browser.cache.offline.enable, general.open_location.last_url, places.history.enabled, browser.formfill.enable, signon.rememberSignons, browser.download.manager.retention, and network.cookie.lifetimePolicy.
In addition, three Firefox patches are needed to prevent disk writes, even if Private Browsing Mode is enabled. We need to prevent the permissions manager from recording HTTPS STS state, prevent intermediate SSL certificates from being recorded, and prevent the content preferences service from recording site zoom. For more details on these patches, see the Firefox Patches section.
Tor Browser Bundle MUST NOT cause any information to be written outside of the bundle directory. This is to ensure that the user is able to completely and safely remove the bundle without leaving other traces of Tor usage on their computer.
FIXME: sjmurdoch, Erinn: explain what magic we do to satisfy this, and/or what additional work or auditing needs to be done.
The Tor Browser MUST prevent a user's activity on one site from being linked to their activity on another site. When this goal cannot yet be met with an existing web technology, that technology or functionality is disabled. Our design goal is to ultimately eliminate the need to disable arbitrary technologies, and instead simply alter them in ways that allows them to function in a backwards-compatible way while avoiding linkability. Users should be able to use federated login of various kinds to explicitly inform sites who they are, but that information should not transparently allow a third party to record their activity from site to site without their prior consent.
The benefit of this approach comes not only in the form of reduced linkability, but also in terms of simplified privacy UI. If all stored browser state and permissions become associated with the url bar origin, the six or seven different pieces of privacy UI governing these identifiers and permissions can become just one piece of UI. For instance, a window that lists the url bar origin for which browser state exists, possibly with a context-menu option to drill down into specific types of state or permissions. An example of this simplification can be seen in Figure 1.
Figure 1. Improving the Privacy UI
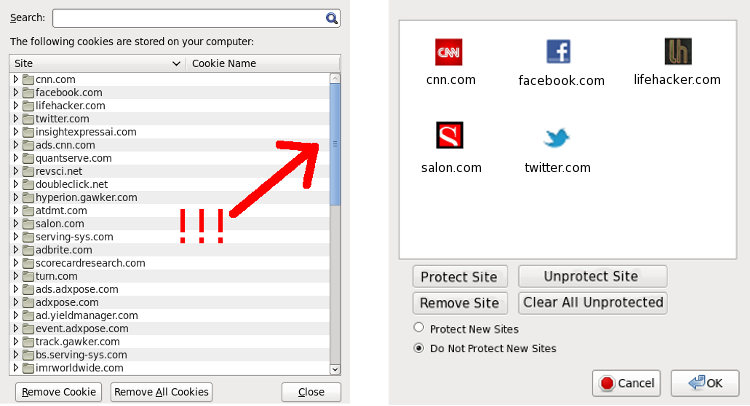
- Cookies
Design Goal: All cookies MUST be double-keyed to the url bar origin and third-party origin. There exists a Mozilla bug that contains a prototype patch, but it lacks UI, and does not apply to modern Firefoxes.
Implementation Status: As a stopgap to satisfy our design requirement of unlinkability, we currently entirely disable 3rd party cookies by setting network.cookie.cookieBehavior to 1. We would prefer that third party content continue to function, but we believe the requirement for unlinkability trumps that desire.
- Cache
Cache is isolated to the url bar origin by using a technique pioneered by Colin Jackson et al, via their work on SafeCache. The technique re-uses the nsICachingChannel.cacheKey attribute that Firefox uses internally to prevent improper caching and reuse of HTTP POST data.
However, to increase the security of the isolation and to solve conflicts with OCSP relying the cacheKey property for reuse of POST requests, we had to patch Firefox to provide a cacheDomain cache attribute. We use the fully qualified url bar domain as input to this field.
Furthermore, we chose a different isolation scheme than the Stanford implementation. First, we decoupled the cache isolation from the third party cookie attribute. Second, we use several mechanisms to attempt to determine the actual location attribute of the top-level window (to obtain the url bar FQDN) used to load the page, as opposed to relying solely on the referer property.
Therefore, the original Stanford test cases are expected to fail. Functionality can still be verified by navigating to about:cache and viewing the key used for each cache entry. Each third party element should have an additional "domain=string" property prepended, which will list the FQDN that was used to source the third party element.
- HTTP Auth
HTTP authentication tokens are removed for third party elements using the http-on-modify-request observer to remove the Authorization headers to prevent silent linkability between domains. We also needed to patch Firefox to cause the headers to get added early enough to allow the observer to modify it.
- DOM Storage
Design Goal: DOM storage for third party domains MUST be isolated to the url bar origin, to prevent linkability between sites.
Implementation Status: Because it is isolated to third party domain as opposed to top level url bar origin, we entirely disable DOM storage as a stopgap to ensure unlinkability.
- Flash cookies
Design Goal: Users should be able to click-to-play flash objects from trusted sites. To make this behavior unlinkable, we wish to include a settings file for all platforms that disables flash cookies using the Flash settings manager.
Implementation Status: We are currently having difficulties causing Flash player to use this settings file on Windows, so Flash remains difficult to enable.
- SSL+TLS session resumption and HTTP Keep-Alive
Design Goal: TLS session resumption tickets and SSL Session IDs MUST be limited to the url bar origin. HTTP Keep-Alive connections from a third party in one url bar origin MUST NOT be reused for that same third party in another url bar origin.
Implementation Status: We currently clear SSL Session IDs upon New Identity, we disable TLS Session Tickets via the Firefox Pref security.enable_tls_session_tickets. We disable SSL Session IDs via a patch to Firefox. To compensate for the increased round trip latency from disabling these performance optimizations, we also enable TLS False Start via the Firefox Pref security.ssl.enable_false_start.
Becuase of the extreme performance benefits of HTTP Keep-Alive for interactive web apps, and because of the difficulties of conveying urlbar origin information down into the Firefox HTTP layer, as a compromise we currently merely reduce the HTTP Keep-Alive timeout to 20 seconds (which is measured from the last packet read on the connection) using the Firefox preference network.http.keep-alive.timeout.
- Automated cross-origin redirects MUST NOT store identifiers
Design Goal: To prevent attacks aimed at subverting the Cross-Origin Identifier Unlinkability privacy requirement, the browser MUST NOT store any identifiers (cookies, cache, DOM storage, HTTP auth, etc) for cross-origin redirect intermediaries that do not prompt for user input. For example, if a user clicks on a bit.ly url that redirects to a doubleclick.net url that finally redirects to a cnn.com url, only cookies from cnn.com should be retained after the redirect chain completes.
Non-automated redirect chains that require user input at some step (such as federated login systems) SHOULD still allow identifiers to persist.
Implementation status: There are numerous ways for the user to be redirected, and the Firefox API support to detect each of them is poor. We have a trac bug open to implement what we can.
- window.name
window.name is a magical DOM property that for some reason is allowed to retain a persistent value for the lifespan of a browser tab. It is possible to utilize this property for identifier storage.
In order to eliminate linkability but still allow for sites that utilize this property to function, we reset the window.name property of tabs in Torbutton every time we encounter a blank referer. This behavior allows window.name to persist for the duration of a link-driven navigation session, but as soon as the user enters a new URL or navigates between https/http schemes, the property is cleared.
- Auto form-fill
We disable the password saving functionality in the browser as part of our Disk Avoidance requirement. However, since users may decide to re-enable disk history records and password saving, we also set the signon.autofillForms preference to false to prevent saved values from immediately populating fields upon page load. Since Javascript can read these values as soon as they appear, setting this preference prevents automatic linkability from stored passwords.
- HSTS supercookies
An extreme (but not impossible) attack to mount is the creation of HSTS supercookies. Since HSTS effectively stores one bit of information per domain name, an adversary in possession of numerous domains can use them to construct cookies based on stored HSTS state.
Design Goal: There appears to be three options for us: 1. Disable HSTS entirely, and rely instead on HTTPS-Everywhere to crawl and ship rules for HSTS sites. 2. Restrict the number of HSTS-enabled third parties allowed per url bar origin. 3. Prevent third parties from storing HSTS rules. We have not yet decided upon the best approach.
Implementation Status: Currently, HSTS state is cleared by New Identity, but we don't defend against the creation of these cookies between New Identity invocations.
- Exit node usage
Design Goal: Every distinct navigation session (as defined by a non-blank referer header) MUST exit through a fresh Tor circuit in Tor Browser to prevent exit node observers from linking concurrent browsing activity.
Implementation Status: The Tor feature that supports this ability only exists in the 0.2.3.x-alpha series. Ticket #3455 is the Torbutton ticket to make use of the new Tor functionality.
In order to properly address the fingerprinting adversary on a technical level, we need a metric to measure linkability of the various browser properties beyond any stored origin-related state. The Panopticlick Project by the EFF provides us with exactly this metric. The researchers conducted a survey of volunteers who were asked to visit an experiment page that harvested many of the above components. They then computed the Shannon Entropy of the resulting distribution of each of several key attributes to determine how many bits of identifying information each attribute provided.
The study is not exhaustive, though. In particular, the test does not take in all aspects of resolution information. It did not calculate the size of widgets, window decoration, or toolbar size, which we believe may add high amounts of entropy. It also did not measure clock offset and other time-based fingerprints. Furthermore, as new browser features are added, this experiment should be repeated to include them.
On the other hand, to avoid an infinite sinkhole, we reduce the efforts for fingerprinting resistance by only concerning ourselves with reducing the fingerprintable differences among Tor Browser users. We do not believe it is productive to concern ourselves with cross-browser fingerprinting issues, at least not at this stage.
- Plugins
Plugins add to fingerprinting risk via two main vectors: their mere presence in window.navigator.plugins, as well as their internal functionality.
Design Goal: All plugins that have not been specifically audited or sandboxed MUST be disabled. To reduce linkability potential, even sandboxed plugins should not be allowed to load objects until the user has clicked through a click-to-play barrier. Additionally, version information should be reduced or obfuscated until the plugin object is loaded.
Implementation Status: Currently, we entirely disable all plugins in Tor Browser. However, as a compromise due to the popularity of Flash, we intend to work towards a click-to-play barrier using NoScript that is available only after the user has specifically enabled plugins. Flash will be the only plugin available, and we will ship a settings.sol file to disable Flash cookies, and to restrict P2P features that likely bypass proxy settings.
- Fonts
According to the Panopticlick study, fonts provide the most linkability when they are provided as an enumerable list in filesystem order, via either the Flash or Java plugins. However, it is still possible to use CSS and/or Javascript to query for the existence of specific fonts. With a large enough pre-built list to query, a large amount of fingerprintable information may still be available.
The sure-fire way to address font linkability is to ship the browser with a font for every language, typeface, and style in use in the world, and to only use those fonts at the exclusion of system fonts. However, this set may be impractically large. It is possible that a smaller common subset may be found that provides total coverage. However, we believe that with strong url bar origin identifier isolation, a simpler approach can reduce the number of bits available to the adversary while avoiding the rendering and language issues of supporting a global font set.
Implementation Status: We disable plugins, which prevents font enumeration. Additionally, we limit both the number of font queries from CSS, as well as the total number of fonts that can be used in a document by patching Firefox. We create two prefs, browser.display.max_font_attempts and browser.display.max_font_count for this purpose. Once these limits are reached, the browser behaves as if browser.display.use_document_fonts was reached. We are still working to determine optimal values for these prefs.
- User Agent and HTTP Headers
Design Goal: All Tor Browser users MUST provide websites with an identical user agent and HTTP header set for a given request type. We omit the Firefox minor revision, and report a popular Windows platform. If the software is kept up to date, these headers should remain identical across the population even when updated.
Implementation Status: Firefox provides several options for controlling the browser user agent string which we leverage. We also set similar prefs for controlling the Accept-Language and Accept-Charset headers, which we spoof to English by default. Additionally, we remove content script access to Components.interfaces, which can be used to fingerprint OS, platform, and Firefox minor version.
- Desktop resolution and CSS Media Queries
Both CSS and Javascript have a lot of irrelevant information about the screen resolution, usable desktop size, OS widget size, toolbar size, title bar size, and other desktop features that are not at all relevant to rendering and serve only to provide information for fingerprinting.
Design Goal: Our design goal here is to reduce the resolution information down to the bare minimum required for properly rendering inside a content window. We intend to report all rendering information correctly with respect to the size and properties of the content window, but report an effective size of 0 for all border material, and also report that the desktop is only as big as the inner content window. Additionally, new browser windows are sized such that their content windows are one of ~5 fixed sizes based on the user's desktop resolution.
Implementation Status: We have implemented the above strategy for Javascript using Torbutton's JavaScript hooks as well as a window observer to resize new windows based on desktop resolution. Additionally, we patch Firefox to cause CSS Media Queries to use the client content window size for all desktop size related media queries.
As far as we know, this fully satisfies our design goals for desktop resolution information.
- Timezone and clock offset
Design Goal: All Tor Browser users MUST report the same timezone to websites. Currently, we choose UTC for this purpose, although an equally valid argument could be made for EDT/EST due to the large English-speaking population density (coupled with the fact that we spoof a US English user agent). Additionally, the Tor software should detect if the users clock is significantly divergent from the clocks of the relays that it connects to, and use this to reset the clock values used in Tor Browser to something reasonably accurate.
Implementation Status: We set the timezone using the TZ environment variable, which is supported on all platforms. Additionally, we plan to obtain a clock offset from Tor, but this won't be available until Tor 0.2.3.x is in use.
- Javascript performance fingerprinting
Javascript performance fingerprinting is the act of profiling the performance of various Javascript functions for the purpose of fingerprinting the Javascript engine and the CPU.
Design Goal: We have several potential mitigation approaches to reduce the accuracy of performance fingerprinting without risking too much damage to functionality. Our current favorite is to reduce the resolution of the Event.timeStamp and the Javascript Date() object, while also introducing jitter. Our goal is to increase the amount of time it takes to mount a successful attack. Mowery et al found that even with the default precision in most browsers, they required up to 120 seconds of amortization and repeated trials to get stable results from their feature set. We intend to work with the research community to establish the optimum trade-off between quantization+jitter and amortization time.
Implementation Status: We have no implementation as of yet.
- Keystroke fingerprinting
Keystroke fingerprinting is the act of measuring key strike time and key flight time. It is seeing increasing use as a biometric.
Design Goal: We intend to rely on the same mechanisms for defeating Javascript performance fingerprinting: timestamp quantization and jitter.
Implementation Status: We have no implementation as of yet.
- WebGL
WebGL is fingerprintable both through information that is exposed about the underlying driver and optimizations, as well as through performance fingerprinting.
Design Goal: Because of the large amount of potential fingerprinting vectors, we intend to deploy a similar strategy against WebGL as for plugins. First, WebGL canvases will have click-to-play placeholders, and will not run until authorized by the user. Second, we intend to obfuscate driver information by hooking getParameter(), getSupportedExtensions(), getExtension(), and getContextAttributes() to provide standard minimal, driver-neutral information.
Implementation Status: Currently we simply disable WebGL.
In order to avoid long-term linkability, we provide a "New Identity" context menu option in Torbutton.
First, Torbutton disables all open tabs and windows by tagging them and blocking them via the nsIContentPolicy, and then closes each tab and window. The extra step for blocking tabs is done as a precaution to ensure that any asynchronous Javascript is in fact properly disabled. After closing all of the windows, we then clear the following state: OCSP (by toggling security.OCSP.enabled), cache, site-specific zoom and content preferences, Cookies, DOM storage, safe browsing key, the Google wifi geolocation token (if exists), HTTP auth, SSL Session IDs, HSTS state, close all remaining HTTP keep-alive connections, and clear the last opened URL field (via the pref general.open_location.last_url). After clearing the browser state, we then send the NEWNYM signal to the Tor control port to cause a new circuit to be created.
Additionally, the user is allowed to "protect" cookies of their choosing from deletion during New Identity by using the Torbutton Cookie Protections UI to protect the cookies they would like to keep across New Identity invocations.
Some content types are too invasive and/or too opaque for us to properly eliminate their linkability properties. For these content types, we use NoScript to provide click-to-play placeholders that do not activate the content until the user clicks on it. This will eliminate the ability for an adversary to use such content types to link users in a dragnet fashion across arbitrary sites.
Currently, the content types isolated in this way include Flash, WebGL, and audio and video objects.
The set of patches we have against Firefox can be found in the current-patches directory of the torbrowser git repository. They are:
- Block Components.interfaces and Components.lookupMethod
In order to reduce fingerprinting, we block access to these two interfaces from content script. Components.lookupMethod can undo our Javascript hooks, and Components.interfaces can be used for fingerprinting the platform, OS, and Firebox version, but not much else.
- Make Permissions Manager memory only
This patch exposes a pref 'permissions.memory_only' that properly isolates the permissions manager to memory, which is responsible for all user specified site permissions, as well as stored HSTS policy from visited sites. The pref does successfully clear the permissions manager memory if toggled. It does not need to be set in prefs.js, and can be handled by Torbutton.
- Make Intermediate Cert Store memory-only
The intermediate certificate store records the intermediate SSL certificates the browser has seen to date. Because these intermediate certificates are used by a limited number of domains (and in some cases, only a single domain), the intermediate certificate store can serve as a low-resolution record of browsing history.
Design Goal: As an additional design goal, we would like to later alter this patch to allow this information to be cleared from memory. The implementation does not currently allow this.
- Add HTTP auth headers before on-modify-request fires
This patch provides a trivial modification to allow us to properly remove HTTP auth for third parties. This patch allows us to defend against an adversary attempting to use HTTP auth to silently track users between domains.
- Add a string-based cacheKey property for domain isolation
To increase the security of cache isolation and to solve strange and unknown conflicts with OCSP, we had to patch Firefox to provide a cacheDomain cache attribute. We use the url bar FQDN as input to this field.
- Randomize HTTP pipeline order and depth
As an experimental defense against Website Traffic Fingerprinting, we patch the standard HTTP pipelining code to randomize the number of requests in a pipeline, as well as their order.
- Block all plugins except flash
We cannot use the @mozilla.org/extensions/blocklist;1 service, because we actually want to stop plugins from ever entering the browser's process space and/or executing code (for example, AV plugins that collect statistics/analyze URLs, magical toolbars that phone home or "help" the user, skype buttons that ruin our day, and censorship filters). Hence we rolled our own.
- Make content-prefs service memory only
This patch prevents random URLs from being inserted into content-prefs.sqllite in the profile directory as content prefs change (includes site-zoom and perhaps other site prefs?).
- Make Tor Browser exit when not launched from Vidalia
It turns out that on Windows 7 and later systems, the Taskbar attempts to automatically learn the most frequent apps used by the user, and it recognizes Tor Browser as a seperate app from Vidalia. This can cause users to try to launch Tor Brower without Vidalia or a Tor instance running. Worse, the Tor Browser will automatically find their default Firefox profile, and properly connect directly without using Tor. This patch is a simple hack to cause Tor Browser to immediately exit in this case.
- Disable SSL Session ID tracking
This patch is a simple 1-line hack to prevent SSL connections from caching (and then later transmitting) their Session IDs. There was no preference to govern this behavior, so we had to hack it by altering the SSL new connection defaults.
- Provide an observer event to close persistent connections
This patch creates an observer event in the HTTP connection manager to close all keep-alive connections that still happen to be open. This event is emitted by the New Identity button.
The purpose of this section is to cover all the known ways that Tor browser security can be subverted from a penetration testing perspective. The hope is that it will be useful both for creating a "Tor Safety Check" page, and for developing novel tests and actively attacking Torbutton with the goal of finding vulnerabilities in either it or the Mozilla components, interfaces and settings upon which it relies.
Torbutton is a complicated piece of software. During development, changes to one component can affect a whole slough of unrelated features. A number of aggregated test suites exist that can be used to test for regressions in Torbutton and to help aid in the development of Torbutton-like addons and other privacy modifications of other browsers. Some of these test suites exist as a single automated page, while others are a series of pages you must visit individually. They are provided here for reference and future regression testing, and also in the hope that some brave soul will one day decide to combine them into a comprehensive automated test suite.
- Decloak.net
Decloak.net is the canonical source of plugin and external-application based proxy-bypass exploits. It is a fully automated test suite maintained by HD Moore as a service for people to use to test their anonymity systems.
- Deanonymizer.com
Deanonymizer.com is another automated test suite that tests for proxy bypass and other information disclosure vulnerabilities. It is maintained by Kyle Williams, the author of JanusVM and JanusPA.
- JonDos
AnonTest
The JonDos people also provide an anonymity tester. It is more focused on HTTP headers and behaviors than plugin bypass, and points out a couple of headers Torbutton could do a better job with obfuscating.
- Browserspy.dk
Browserspy.dk provides a tremendous collection of browser fingerprinting and general privacy tests. Unfortunately they are only available one page at a time, and there is not really solid feedback on good vs bad behavior in the test results.
- Privacy
Analyzer
The Privacy Analyzer provides a dump of all sorts of browser attributes and settings that it detects, including some information on your original IP address. Its page layout and lack of good vs bad test result feedback makes it not as useful as a user-facing testing tool, but it does provide some interesting checks in a single page.
- Mr. T
Mr. T is a collection of browser fingerprinting and deanonymization exploits discovered by the ha.ckers.org crew and others. It is also not as user friendly as some of the above tests, but it is a useful collection.
- Gregory Fleischer's Torbutton and
Defcon
17 Test Cases
Gregory Fleischer has been hacking and testing Firefox and Torbutton privacy issues for the past 2 years. He has an excellent collection of all his test cases that can be used for regression testing. In his Defcon work, he demonstrates ways to infer Firefox version based on arcane browser properties. We are still trying to determine the best way to address some of those test cases.
- Xenobite's
TorCheck Page
This page checks to ensure you are using a valid Tor exit node and checks for some basic browser properties related to privacy. It is not very fine-grained or complete, but it is automated and could be turned into something useful with a bit of work.